 |
Breast Cancer Nutrition |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
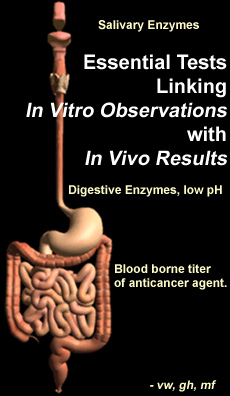 |
When considering the effects of diet on cancer prevention it is important to understand the gauntlet that both foodstuffs and medication must run before appearing in the molecule. First, salivary enzymes such as amylase begin to break down certain carbohydrates into simpler sugars. Then in the stomach, acid conditions and proteolytic enzymes break up long amino acid chains into their smaller components. Then in the colon these partially broken down substances are taken to the liver where they are subjected to a multitude of biochemical pathways that detoxify, rearrange and alter the structure of the consumed material. This chemistry is exceedingly complex and adaptive. The body has special adaptive mechanisms that enable the chemistry to create tailor made detoxifications. This makes the long term effects of nutrition and medication difficult to predict and control. |
|
|
|
|
herbs
picture.
|
What
happens in the body is much different than what happens in the
test tube. Nevertheless, the following substances do inhibit growth
of cancer cells in culture, this does not mean they affect the
growth of cells in the body, for the reasons mentioned above.
|
|
|
|
|
link
to NCI nutrition book.
|
|
|
|
|
|
link
to pathways.
|
Pathways B-12 Folate Metabolism
R-bind Bind to intrinsic factor Bind to trans cobalamin II |
|
|