|
|||||||||||||
|
NSAID Analgesics (and Acetaminophen) |
|||||||||||||
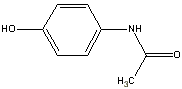
Acetaminophen,
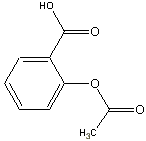
aspirin, and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or NSAID's are
grouped together because they have similar analgesic potency. NSAID's
are effective for relief of mild pain and have opioid dose sparing effects
that help reduce opioid side effects when given with an opioid for moderate
to severe pain.
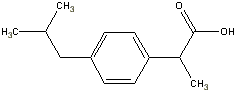
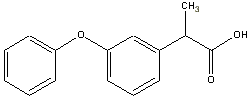
NSAID Mechanisms of ActionAspirin, NSAID's and acetaminophen come in long acting (12 hour release forms. Aspirin also comes in an enteric coated form. Combining any of these with a muscle relaxant enhances bone or joint pain relief. Acetaminophen is less effective than aspirin or many NSAID's. Aspirin and NSAID's block the biosynthesis of prostaglandins in peripheral tissues by blocking the enzyme cyclooxygenase, which converts arachidonic acid to prostaglandins Acetaminophen acts centrally. These agents can effectively be used in adults and children. |
|||||||||||||
| NSAID Analgesics - Prescription | |||||||||||||
NSAID DosageUse patient response to determine effective dosing. If pain is uncontrolled with the maximum dosage of one NSAID, try another drug within the same category before abandoning NSAID therapy. Refer to the pediatric section for appropriate dosing in children.
NSAID AdministrationThe drugs in this group are primarily oral (tablets, capsules, liquid) Only acetaminophen is available in suppositories Only Ketorolac is available for parental use, but it is only recommended for 3-4 days because of GI toxicities, thus its usefulness in cancer pain is limited. NSAID Contraindications and Side EffectsContraindicated in patients with thrombocytopenia. Patients taking NSAID's (except acetaminophen) are at risk for platelet dysfunction. Refer to Table 4 for a list of NSAID's with minimal antiplatelet activity. Side Effects (believe to occur as a consequence of cyclooxygenase inhibition) Renal failure (primarily with NSAID's) Hepatic dysfunction (primarily with acetaminophen at doses above 5000 mg/day) Bleeding secondary to platelet dysfunction Gastric ulceration. |
|||||||||||||
|
Dosage |
|||||||||||||
|
Note 0: Only drugs that are FDA approved as an analgesic for use in children
are included. Note 1: Acetaminophen and NSAID dosages for adults weighing less than 50 kg should be adjusted for weight. Note 2: Relative Potency may be viewed as how the a particular substance, rendered in blue, "stacks up" in potency against a morphine standard, rendered in red. Note 3: Asingle unadorned letter "h" is the standard metric abbreviation for hour, "kg" is the abbreviation for kilogram. Note 4: Ref: Source of Dosage Guidelines Roxanne Laboratories Pain Institute Note 5: You can modify these drug structures and search for the resulting compound using this plug-in. |
|||||||||||||