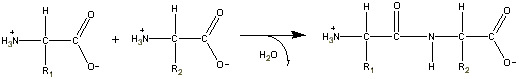|
9/16/99
|
HP Dr. Drake
|
Biochemistry
|
Summary Notes
|
L. Van Warren
|
|
Chapter 4
Amino Acids
|
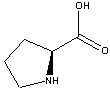
Proline
|
- There are 20 amino acids.
- They are called the a
amino acids.
- Except for Proline they all have a primary amino
group and a carboxylic acid group on the same carbon
1.
The Amino Acids of Proteins
A. General Properties
- pK1 is the a-carboxylic
acid and
- pK2 is the a-amino group
and
- pKr are the side groups
with acid base properties
- In the physiological pH range, both the carboxylic
acid and the amino groups of the a-amino acids are completely ionized.
- Molecules that bear charged roups of opposite
polarity are known as zwitterions or dipolar ions.
B. Peptide Bonds
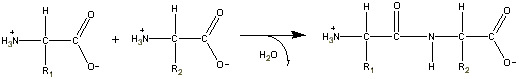
- The CO-NH linkage is known as a peptide bond.
- Short peptides of length 2, 3 and a few an many
are known as
dipeptides, tripeptides, oligopeptides and polypeptides.
- Proteins are molecules that consist of one or
more polypeptide chains.
- Polypeptides are linear polymers.
- The various organisms on Earth collectively syntheisze
an enormous number of different protein molecules whose great range of physicochemical
characteristics stem largely from the varied properties of the 20 "standard"
amino acids.
C. Classification and Characteristics
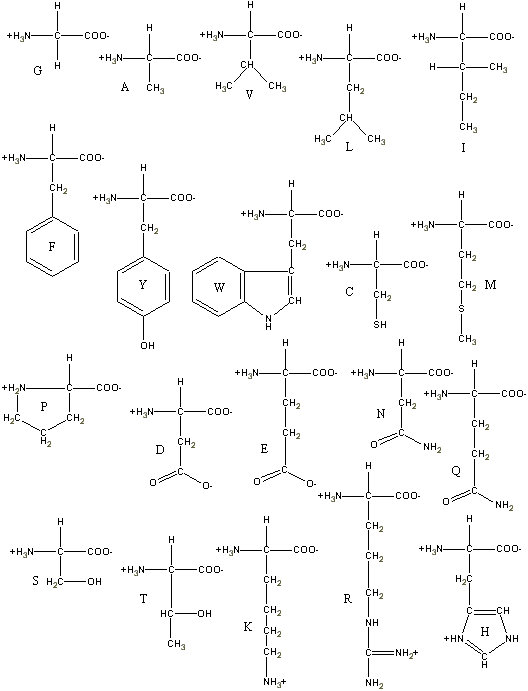
- There are three classes of amino acids.
- 1) those with nonpolar R groups
- 2) those with uncharged polar R groups
- 3) those with charge polar R groups
- The Nonpolar Amino Acid Side Chains Have
a Variety of Shapes and Sizes
- G,A V, L I, M, P, F, W
- Uncharged Polar Side Chains Have Hydroxyl, Amide,
or Thiol Groups
- S, T, N, Q, T, C
- Cysteine has great importance, it can join separate
polypeptide chains or cross-link two cysteines in the same chain.
- Charged Polar Side Chains May Be Positively or
Negatively Charged
- K, R, H, D, E
- The basic amino acids are KRH
- The acidic amino acids are DE
- The hydroxylic amino acids are Serine, Threonine,
and Tyrosine
- Only histadine with pKr=6.0 ionizes within the
physiological pH range.
- Histadine side chaings often participate in the
catalytic ractions of enyzmes.
- The 20 amino acids vary considerably in thier
physicochemical properties such as polarity, acidity, basicity, aromaticity,
bulk, conformational flexibility, crosslinkability, hydrogen bonding and chemical
reactivity. These several characteristics are largely responsible for protein's
great range of properties.
D. Acid-Base Properties
pH = pK + log([A-]/[HA])
- Amino acids and proteins have conspicuous acid
base properties.
- Amino Acids never assume the neutral form in
aqueous solution.
- pI = 1/2(pKi + pKj) where Ki and Kj are the dissociation
constants of the two ionizations involving the neutral species.
- Proteins Have Complex Titration Curves
E. A Few Words on Nomenclature
- Glx means Glu or Gln
- Asx means Asp or Asn
2. Optical
Activity
- except for glycine all the amino acids are optically
active.
- Optically active molecules have an asymmetry
such that they are not superimposable on their mirror image in the same way
that a left hand is not superimposable on its mirror image, a right hand.
- Left and right hand corresponding molecules are
called enantiomers.
- Only when probed by plane polarized light or
by reactants that thave chiral centers can they be distinguished or manipulated.
A. An Operational Classification
- Molecules are classified as dextrorotatory (right)
or levorotatory (left)
- A polarimeter measures the optical activity as
specific rotation.
- Proline, leucine and arginine have specific rotations
of -86.2, -10.4 and +12.5 degrees.
- So it is conceivable that pure substance identification
could be done with a polarimeter, and that mixed sample identification could
be done, with simultaneous solution of equations.
- d (dextro) and l (levo).
B. The Fischer Convention
- Molecules are classified as dextrorotatory (right)
or levorotatory (left)
- Horizontal bonds extend above the plane of the
paper.
- Vertical bonds extend below the plane of the
paper.
- All a-amino acids derived from proteins have
the L stereochemical configuration.
- The CORN crib mnemonic.
- Diastereomers Are Chemically and Physically Distinguishable
C. The Cahn - Ingold - Prelog System
- Atoms of hinger atomic number bonded to a chiral
center are ranked above those of lower atomic number.
- The order of prioriy of some common functional
groups is:
SH > OH > NH2 > COOH > CHO > CH2OH
> C6H5 > CH3
> 2H > 1H
- If the order of groups W --> X --> Y as
seen from the direction is clockwise, then the configuration of the asymmetric
center is designated (R) (Latin: rectus, right). If the order of W -->
X --> Y is counterclockwise, the asymmetric center is designated (S) (Latin:
sinistrus, left).
- A major advantage of teh Cahn-Ingold-Prelog or
RS system is that the chiralities of compounds with multiple asymmetric centers
can be unambiguously described.
- Prochiral Centers Have Distinguishable Substituents
- Two chemically identical substituents to an otherwise
chiral tetrahedral center are geometrically distinct.
- Planar objects with no rotational symmetry also
have the property of prochirality.
D. Chirality and Biochemistry
- Ordinary chemical synthesis produces racemic
mixtures.
- The biosynthesis of a substance possessing asymmetric
centers almost invariably produces a pure stereoisomer.
3. "Nonstandard"
Amino Acids
A. Amino Acid Derivatives in Proteins
- In all known cases but selenocysteine, the other
amino acids which are components of proteins result from the specific modification
of an amino acid residue after the polypeptide chain has been synthesized.
- Among these are 4-hydroxyproline and 5-hydroxylysine,
both of which are important constituents of collagen.
- Ribosomal proteins known as histones may be methylated,
acetylated, or phosphorylated.
B. Specialized Roles of Amino Acids
- Nature tends to adapt materials and processes
tht are already present to new functions.
- Certain amino acids are important intermediates
in various metabolic processes.